The Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT) is vital in evaluating prospective graduate students, especially those eyeing business administration and related master’s programs. This standardized assessment measures cognitive abilities in quantitative reasoning, verbal communication, analytical writing, and integrated reasoning. Beyond gauging academic prowess, the GMAT serves as a reliable predictor of a candidate’s aptitude for success in the challenging environment of a master’s program.
This guide provides clarity and guidance on navigating the GMAT, offering meticulous preparation materials and insights into institutions with holistic admissions approaches. Join us on this journey to empower you for GMAT success and unlock doors to prestigious graduate programs aligned with your aspirations.

Table Of Contents
What is GMAT?
The Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT), administered by the Graduate Management Admission Council (GMAC) online or at a test center, is a standardized evaluation tool. Widely adopted by business universities globally, the GMAT assesses students’ readiness for business degree programs, including Master of Business Administration (MBA) and other graduate degrees such as Finance, Marketing, and Accounting. While the primary use of GMAT scores is for admission into business graduate programs, organizations may also request them for hiring.
Typically, universities consider GMAT scores from the past five years, recognizing that recent performance is a relevant indicator of a candidate’s current capabilities. A high GMAT score enhances applicants’ chances of admission into graduate programs and positively influences their overall application. As a comprehensive assessment tool, the GMAT is crucial in evaluating candidates’ aptitude and suitability for success in various business-related disciplines.
GMAT Test: Basic Information
The Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT) is a pivotal standardized online test conducted by the Graduate Management Admission Council (GMAC). Widely acknowledged by business universities globally, GMAT is essential for assessing candidates seeking admission to various business graduate programs, including Master of Business Administration (MBA). In this brief overview, we’ll explore critical information about the GMAT, its significance, and its role in shaping aspiring graduate students’ academic and professional trajectories.
How much does the GMAT cost?
Every student planning to take the GMAT exam is required to pay a registration fee, which varies by country. Additionally, several other GMAT exam costs are associated with specific needs, such as rescheduling, requesting additional score reports, etc. Below is a detailed breakdown of GMAT fees and expenses.
1. GMAT Registration Fee
- The current GMAT examination fee is USD 250.
- Additional taxes may apply in specific countries, as the official GMAT exam website mentions.
2. GMAT Rescheduling Fee
- Rescheduling fees apply if you modify your exam date.
- The amount varies based on the number of days before the exam date:
- More than 60 days: $50
- 15-60 days: $100
- 2-14 days: $150
3. GMAT Cancellation Fee and Refund Policy
- You may be entitled to a refund if you cancel your GMAT appointment.
- Refund amounts vary based on the number of days before the exam date:
- More than 60 days: $100
- 15-60 days: $75
- Less than 14 days: $50
Note: No rescheduling or cancellation is allowed 24 hours before the exam date, and forfeiting the entire GMAT exam fee is mandatory.
4. Additional GMAT Fees
Optional services may incur additional fees, applicable each time the service is requested:
| Additional Services | GMAT Test Cost |
|---|---|
| Additional Score Report | $35 per report |
| Enhanced Score Report | $30 |
| AWA Essay Rescoring | $45 |
| Cancel Score (After leaving the test center) | $25 |
| Reinstate Score | $50 |
Total Costs Calculation:
- The total costs of taking the GMAT vary based on individual circumstances.
- Example Calculation:
| Type of Cost | Amount |
|---|---|
| GMAT Registration Fee | $250 |
| GMAT Preparation Course Fees | $349 |
| Rescheduling GMAT Appointment | $50-$150 |
| Requesting Additional Score Reports | $35 per report |
| Retaking the Exam | $250 |
- Total GMAT Price (Example): $774 (for a well-performed first attempt) or higher based on specific needs.
Minimizing GMAT Costs
- To minimize costs, prepare thoroughly for the exam and aim for success on the first attempt.
- Book your exam slot well in advance to avoid rescheduling fees.
- Start preparation early and only request additional voluntary services when necessary to reduce GMAT costs.
When to take GMAT?
The best time to take the GMAT (Graduate Management Admission Test) depends on several factors, including your application deadlines, preparation level, and personal schedule. Here are some general guidelines to help you decide when to take the GMAT:
- Application Deadlines
Determine the application deadlines for the business schools you’re interested in. Plan to take the GMAT with enough time to receive your scores before these deadlines. - Preparation Time
Assess your current level of preparation. Most candidates need several weeks to months of study to perform well on the GMAT. Consider your other commitments and plan accordingly. - Retake Option
Remember that you can retake the GMAT if you are unsatisfied with your initial score. However, there is a waiting period between attempts, so factor this into your planning. - Peak Performance
Schedule the test when you believe you’ll be at your cognitive peak. Some people perform better in the morning, while others are more alert in the afternoon or evening. Choose a time that aligns with your natural energy levels. - Score Validity
GMAT scores are valid for five years. Consider this timeframe if you plan to apply to business school a few years after taking the test. - Application Cycle
Understand the application cycles of the business schools you’re interested in. Some have multiple application rounds, while others have rolling admissions. Plan to take the GMAT early enough to meet the requirements of your preferred application round. - Personal Readiness
Ensure you are mentally and emotionally prepared to take the test. Avoid scheduling the GMAT during stressful periods in your personal or professional life. - Test Center Availability
Check the availability of test dates at your preferred test center. Some locations may have limited slots, especially during peak times.
GMAT Sections
The GMAT (Graduate Management Admission Test) consists of four main sections, each designed to assess different skills. Here’s an overview of the GMAT section
Analytical Writing Assessment (AWA)
Time: 1 topic in 30 minutes
The AWA section evaluates your ability to analyze the reasoning behind a given argument and express your thoughts in a coherent and well-organized essay. You’ll be presented with an argument and critique its logical soundness.
Integrated Reasoning (IR)
Time: 12 questions in 30 minutes
The IR section measures your ability to analyze and synthesize information from different sources. Questions involve graphics interpretation, table analysis, multi-source reasoning, and two-part analysis. This section tests your skills in data interpretation and reasoning.
Quantitative Reasoning
Time: 31 questions in 62 minutes
The Quantitative section assesses your ability to analyze data and draw conclusions using mathematical reasoning. Questions cover arithmetic, algebra, geometry, and data analysis. The section includes problem-solving and data-sufficiency questions.
Verbal Reasoning
Time: 36 questions in 65 minutes
The Verbal section evaluates your ability to analyze and evaluate written material. It includes three questions:
- Reading Comprehension: Assessing your ability to understand and analyze information from passages.
- Critical Reasoning: Testing your ability to evaluate arguments and make well-reasoned decisions.
- Sentence Correction: Evaluating your proficiency in sentence structure and grammar.
GMAT Test Registration
Follow these steps to register for the GMAT (Graduate Management Admission Test).
- Create a GMAT Account
Go to the official GMAT website (GMAC website). Click “Register” or “Sign Up” to create a user account. - Choose a Test Center and Date
Log in to your GMAT account. Select your preferred test date and location. GMAT is offered at various test centers around the world. - Complete the Registration Form
Fill in the required personal information, including your name, contact details, and educational background. - Agree to Terms and Conditions
Review and agree to the terms and conditions for taking the GMAT. - Payment
Pay the GMAT exam fee. The cost of the GMAT exam is around $275-300. Prices may vary, and additional fees for rescheduling or other services may apply. - Confirmation
Once your payment is processed, you’ll receive a confirmation email with details about your test appointment. - Prepare for the Exam
Use the time leading up to your test date to prepare. Consider using official GMAT study materials, practice exams, and other resources to familiarize yourself with the format and content of the test. - Day of the Exam
On the exam day, arrive at the test center on time. Bring valid, government-issued photo identification (e.g., passport) with you.
Note: The GMAT is offered year-round, and you can take the test once every 16 calendar days, up to five times in a rolling 12-month period. Be mindful of application deadlines for the business schools you are interested in, and plan your test date accordingly.
GMAT Format
The GMAT exam is structured into four sections:
- Analytical Writing
- Integrated Reasoning
- Quantitative Reasoning
- Verbal Reasoning.
Test-takers can choose the order of these sections from three available options:
- Option 1: Analytical Writing, Integrated Reasoning, Quantitative Reasoning, Verbal Reasoning
- Option 2: Verbal Reasoning, Quantitative Reasoning, Integrated Reasoning, Analytical Writing
- Option 3: Quantitative Reasoning, Verbal Reasoning, Integrated Reasoning, Analytical Writing
The total duration of the GMAT exam is 3 hours and 7 minutes. The entire test is computer-based, and it’s important to note that once you move on to the next question, you cannot go back to the previous one. The GMAT is a computer-adaptive test, meaning that the difficulty level of the questions adapts based on your performance. If you answer a question correctly, the subsequent question will be slightly more challenging, and vice versa.
Breakdown of each section
| Section | Description | Questions | Score Range | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analytical Writing | Analysis of an Argument | 1 | 0-6 | 30 minutes |
| Integrated Reasoning | Graphics Interpretation, Table Analysis, Multi-source Reasoning, Two-part Analysis | 12 | 1-8 | 30 minutes |
| Quantitative Reasoning | Data Sufficiency, Problem-Solving | 31 | 6-51 | 62 minutes |
| Verbal Reasoning | Reading Comprehension, Critical Reasoning, Sentence Correction | 36 | 6-51 | 65 minutes |
The total GMAT score ranges from 200 to 800, representing a scaled Quantitative and Verbal sections score. Analytical Writing and Integrated Reasoning scores are reported separately on the scorecard.
Additional information:
- Total Time: 3 hours and 7 minutes
- Optional Breaks: 2 breaks of 8 minutes each
How to Prepare for GMAT
Preparing for the GMAT is not tricky. First, it is crucial to understand each exam section and what those sections are testing. And then create a GMAT preparation strategy.
Here are 15 Top strategies and steps to help you prepare for the GMAT overall
- Understand the GMAT Format
Familiarize yourself with the format, sections, and question types of the GMAT. Knowing what to expect will help you plan your study strategy. - Set a Realistic Study Schedule
Plan your study schedule well before your test date. Consider your strengths and weaknesses, and allocate more time to challenging sections. - Use Official GMAT Materials
Utilize official GMAT study materials on the official GMAT website, such as the GMAT Official Guide, GMATPrep software, and other resources. - Take a Diagnostic Test
Begin your preparation by taking a diagnostic test to assess your baseline performance. This will help you identify areas that need improvement. - Focus on Weak Areas
Concentrate on your weaker areas and maintain regular practice in all sections. Allocate more time to topics that you find challenging. - Utilize Test Prep Resources
Explore other reliable test prep materials, such as review books, online courses, and practice exams. Many commercial providers offer GMAT prep courses. - Create a Study Plan
Develop a study plan that covers all sections of the GMAT. Break down your study sessions into manageable time blocks and set specific goals for each session. - Practice Time Management
Since the GMAT is a timed test, practice time management during your study sessions. Simulate test conditions to improve your pacing. - Take Full-Length Practice Tests
Take full-length practice tests to simulate the actual testing experience. Analyze your performance, identify patterns of mistakes, and adjust your study plan accordingly. - Review Mistakes Thoroughly
After each practice session or practice test, review your mistakes carefully. Understand the underlying concepts and develop strategies to avoid similar errors in the future. - Build Mental Stamina
The GMAT is a lengthy test, so build your mental stamina by taking practice tests in a distraction-free environment. - Seek Additional Help if Needed
If you find specific topics challenging, consider seeking additional help. This could be through tutoring, online forums, or study groups. - Stay Healthy
Maintain a healthy lifestyle during your preparation. Get enough sleep, exercise regularly, and eat well to ensure optimal cognitive function. - Take Breaks
Incorporate breaks into your study sessions to prevent burnout. Short breaks can help you stay focused and maintain productivity. - Stay Positive
Stay positive and believe in your ability to improve. Consistency and a positive mindset are crucial to success.
We will walk you through particular GMAT sections, provide sample questions, and how to tackle these sections.
Analytical Writing
Analytical Writing is a section in which you are tested for your analytical abilities to read a given argument and develop your analysis. You will be presented with one argument, and you have 30 minutes to perform that analysis and type up your analysis. The scoring range is 0-6. Your analysis should include your thoughts on what the argument lacks, loopholes in that argument, and how to improve that argument, or provide an alternative way of that argument.
You will be given one argument and have 30 minutes to write your critique. Your response should be well-organized and justify the points in your analysis with well-written support. Your critical-thinking abilities and communication analysis are tested and scored.
GMAT Sample Questions – Analytical Writing
“People should not be misled by the advertising competition between Coldex and Cold-Away, both popular over-the-counter cold medications that anyone can purchase without a doctor’s prescription. Each brand accuses the other of causing some well-known, unwanted side effects: Coldex contributes to high blood pressure, and Cold-Away is known to cause drowsiness. But the choice should be clear for most health-conscious people: Cold-Away has been on the market for much longer and is used by more hospitals than Coldex. Cold-Away is more effective.”
Source: ExamFocus.com
“Most companies would agree that as the risk of physical injury occurring on the job increases, the wages paid to employees should also increase. Hence, it makes financial sense for employers to make the workplace safer: they could thus reduce their payroll expenses and save money. Discuss how well-reasoned you find this argument. In your discussion, analyze the line of reasoning and the use of evidence in the argument. For example, you may need to consider what questionable assumptions underlie the thinking and what alternative explanations or counterexamples might weaken the conclusion.
You can also discuss what evidence would strengthen or refute the argument, what changes would make it more logically sound, and what, if anything, would help you better evaluate its conclusion.”
Source: MBA.com
How to prepare for Analytical Writing?
The best way to prepare for the Analytical Writing section is by understanding the intent of the Analytical section. And how this section is scored. The Analytical Writing section is not intended to test your opinion on the topic or which side you might want to take on the provided argument. But the intent is to check your analyzing skills and how you communicate your analysis.
It is important to note that whichever side of the argument you are on, you should frame your answer to support that side only and not flip-flop in your analysis. We recommend that you follow the below steps.
- You should first read the provided argument thoroughly
- Clearly understand the argument
- Write down the strengths and weaknesses in the argument
- Write down
- Create a structure of your answer following this format
- Introduction
- State each critique point and a case supporting your critique (like why, how, etc.)
- See if you can poke a hole in the presented argument by highlighting what points the argument is missing and what can add value to the given argument
- Provide your analysis of what would have strengthened the provided argument.
- Conclusion
- Proofread your answer for the following
- Grammatical mistakes
- Typos
- Effective organization of your answer
- Check direct/indirect communication
- Finally, make sure that your answer follows the format mentioned above, which is. Introduction> Your critique and support of your critique > Holes in the presented argument and how that argument can be strengthened > Conclusion
It is essential to practice a lot. Follow the above method dozens of times before your exam day, and you will score a perfect 6.0 in the Analytical Writing section.
Integrated Reasoning
Integrated Reasoning is a section that tests your ability to read and understand all the provided data and solve a problem using that data. The data can be provided through graphics, tables, graphs, numbers, or text. You will have to answer 12 questions within 30 minutes. The scoring range is 1-8.
There are four types of questions that you will face.
- Multi-source Reasoning
- Table Analysis
- Graphics Interpretation
- Two-part analysis
GMAT Sample Questions – Integrated Reasoning
Sample Question for Multi-source Reasoning
Sample Question for Table Analysis
Sample Question for Graphics Interpretation
Sample Question for Two-Part Analysis
How do I prepare for Integrated Reasoning?
The Integrated Reasoning section aims to see how well you can integrate all the provided data and interpret that data to solve problems. Your ability to see relationships between different data points will be tested.
- You need to read carefully and digest all the presented data.
- The data might be using different units of measurement, and you need to keep an eye on it and quickly convert all the data to be in the same units.
- When the data is presented in a table form, you can use the sorting functionality on the top, which might save you some time.
- You should practice reading graphs. Keep an eye out for the accompanying text.
- Look if there is any relationship between various data points and see if there is any trend.
- You can use an on-screen calculator.
- Look for the labels used on the graphs.
- Always remember to look for individual numbers and percentages.
- And finally, just like other sections, remember to practice a lot before the exam.
Quantitative Reasoning
In the Quantitative Reasoning section, you will be tested for your ability to solve problems mathematically, interpret data, and use quantitative skills. This section needs some math knowledge, especially in algebra, geometry, and basic arithmetic. The math is not that difficult and is not the section’s emphasis. But the real test is how you use the provided data and your quantitative skills to solve a given problem. There are 31 questions in this section, and you have 62 minutes for this section. There are two main types of questions –
- Problem Solving
- Data Sufficiency
GMAT Sample Questions – Quantitative Reasoning
Here are a couple of sample questions and answers for the Quantitative Reasoning section
A sample question for the Problem-Solving type of question
A sample question for the Data Sufficiency type of question
How to prepare for Quantitative Reasoning?
The Quantitative Reasoning section can look daunting for a lot of people, especially for people who don’t have a math background. However, it is essential to note that this section will be scored based on your quantitative ability. But if you are good at high school math, it will help save time on exam day. Note that calculators are not available during the exam. So, brushing up your math knowledge long before the exam and practicing the math questions is essential.
We recommend reading, understanding, and practicing algebra, geometry, and graphical calculations. We also recommend that you develop a process for solving each problem. Many people create their own method of going through a quantitative problem.
| Here is one helpful procedure in solving quantitative problems |
| Read- the provided data. |
| Understand – Is there anything you can see more than what is stated from each piece of data? |
| Normalize – Convert all data into the same types of units (e.g., all time can be in seconds instead of some variables using hours, or all lengths can be in meters instead of a mix of units) |
| Standardize – Convert all language and data into one type. For example – if there is any mention of time taken in language, like “Person B took half of what Person A took,” convert that into an equation. B = A/2 |
| Imagine – look at the provided visuals and data. Imagine how the visual would look for that data or how the visual would look in data form. This way, you get a perspective of what fits where. |
| Solve – Attempt to solve the problem. |
Other tips
- Use the elimination method to eliminate possibilities and narrow down the correct answer
- Establish dependencies within the provided data
- Evaluate each statement separately
- Calculators are not allowed. So, it is essential to practice basic math to save time in the exam.
Verbal Reasoning
The verbal Reasoning section tests your ability to read, understand, evaluate arguments, and communicate effectively using proper English. It is essential to note that the section does not look to test your knowledge on a given topic, sentence, or subject matter expertise on issues. But this section only tests your ability to grasp the given text’s meaning and fix the sentences. You have 65 minutes for this section.
The section contains 36 questions, which are split into the following areas.
A) Reading Comprehension
- You will be presented with a passage, and you will be given questions about the passage.
- You will be asked to summarize the passage and describe the author’s tone, or you will be asked to draw inferences based on the provided text.
- The subject of the passage varies from social issues, humanities, business-related topics, etc.
B) Critical Reasoning
- In this type of question, you will be given an argument or set of statements.
- Questions are intended to test your ability to make/evaluate arguments, present your case, or assess a presented situation.
C) Sentence Correction
- These types of questions test your language skills
- There are two types of questions within this.
- Correcting sentences for grammar and structure.
- Modifying sentences for better and concise communication, grammar, and structure.
GMAT Sample Questions – Verbal Reasoning
A sample question for Reading Comprehension
Sample Critical Reasoning Question
Sample Sentence Correction Question
How to prepare for Verbal Reasoning?
One of the best ways to tackle this section is to read and understand the meaning of the provided text thoroughly. There is a difference between merely reading and understanding. When you spend time understanding the provided text, you can easily infer other things from that text, and this is where the focus of the section is.
After this step, all your language skills will let you rephrase a given sentence for concise communication or a better structure. Language skills can be improved by reading a lot of formal writing – newspapers, technical journals, etc. It is important to note that your vocabulary is not a test, but it is your grasping power. It is being tested.
You should expect some sentences to be very long and complicated. Breaking down these sentences into smaller parts will help you understand them quickly. You will need to practice the process of breaking down before the exam.
Finally, just like other tests or sections, you must practice much for the verbal reasoning section. Read a lot of material with elaborate descriptions, learn to spend less time on shorter sentences, and use that saved time on long and complicated sentences.
Best way to prepare for GMAT
Methodically preparing for the GMAT yields the best results. Every person has different abilities, strengths, and weaknesses. There is no secret way to prepare for the GMAT. However, studies have shown that if you devise a plan for designing and implementing that plan, it will make a lot of difference.
Here is a 6-step plan that we recommend.
Step 1 – Set a GMAT target score
Be realistic about your goal. The GMAT score requirements might vary from school to school. So, set up a real goal depending on which school you want to apply for. Many people do that more than six months before the exam date. This gives you ample time to prepare to meet that goal.
Step 2 – Take mock GMAT tests
Sign up for at least three complete GMAT tests. Take the tests and analyze your results. The average of 3 tests is where you can expect to score without accurate preparation.
Step 3- Measure the gap
Measure the gap between your target score and the average score for each section of the GMAT. Now you know where you stand versus where you want to be.
Step 4 – Set preparation goals and timelines
Based on your schedule, determine how many hours per week you can allocate toward prepping for the exam. Note that studies have shown that there is a correlation between the number of hours spent on the exam and the achieved score.
The Graduate Management Admission Council (GMAC) studied test-takers and found that 21% of total test-takers spent 20 hours or less in preparation. 23% percent spent between 21 to 50 hours of preparation. 28% spent between 51 to 100 hours. And another 28% spent 101 hours or more. See the below chart from MBA.com.
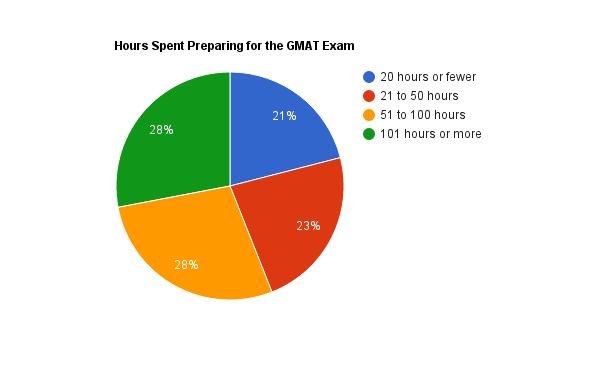
Also, the GMAC found a direct correlation between hours spent and achieved scores. See the below graph from MBA.com.
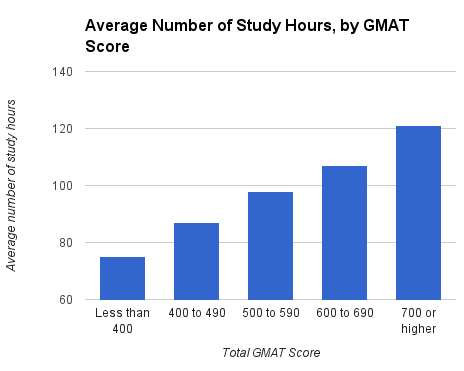
Source: MBA.com
Given all this, you must allocate appropriate study hours for the GMAT. You can use the interactive tool provided for the GMAT exam by providing your desired GMAT target score, the hours per week you can dedicate to the GMAT exam, and the region from where you are applying for GMAT, and get an estimated required study time and also receive s study plan tailored with accordance to your available time. Check out more information on how to study for GMAT.
Step 5 – Sign up for the exam.
By now, you already know how many days/weeks/months are needed to achieve your GMAT goal. Sign up for the exam based on that timeline and available GMAT dates.
Step 6 – Start executing the preparation plan
Start executing the plan by allocating calendar time toward the preparation. Don’t forget to take more mock tests at regular intervals to measure your progress.
GMAT Study
Different people have adopted various strategies concerning what to study as part of the preparation. Multiple choices are available for GMAT study, such as study apps, GMAT prep books, online classes, tutors, etc. We have compiled a list of such resources below
GMAT Apps
- MBA.com – MBA.com offers a GMAT Prep App that costs $4.99. The App consists of questions from the previous GMAT tests and answers with a full explanation.
- Magoosh – Magoosh is a free app for GMAT Prep and Practice. Magoosh provides video lessons and practice questions. In the premium version, Magoosh delivers a lot more content for preparation that includes many more video lessons, practice tests, progress trackers, etc.
GMAT Tutors
- Economist – Economist GMAT Tutor is a private tutor service that provides one-on-one tutoring sessions with expert tutors. They also offer thousands of practice questions. This tutoring service comes with three different tiers – Complete Prep, Premium Prep, and Ultimate Prep, with costs ranging from $799 to $1099.
- Princeton – Princeton GMAT Private Tutoring provides 1:1 tutoring sessions, video lessons, and practice materials. There are two tiers of tutoring – GMAT Comprehensive Private Tutoring, which has a price tag of $167/hour, and GMAT Targeted Private Tutoring, which costs $180/hour.
GMAT Prep Books
- McGraw-Hill – This is an all-in-one GMAT Prep book that reviews all aspects of the GMAT test. The book also includes practice questions, tips, and scoring techniques.
- Kaplan – Kaplan’s GMAT Prep Plus book provides comprehensive GMAT preparation material with more than 2000 practice questions, answers, explanations, strategies, and full-length tests.
GMAT online practice tests
- Manhattan – Manhattan Prep provides one GMAT practice test. They also offer six full-length Practice tests and assessment reports. The 6 test pack costs $49.
- Veritas – Veritas Prep provides one free full-length practice test. Veritas also provides seven full-length practice tests for a discounted price of $19 in April 2020, and the regular price is $49.
GMAT Videos
- YouTube GMAT – Many GMAT Prep courses are available on YouTube. Professionals with a ton of experience in GMAT create some of these videos. Simply search for GMAT Prep on YouTube and find many resources. Here is one such video resource.
- Khan Academy GMAT – Khan Academy is a popular GMAT prep video. Khan Academy provides many Problem Solving and Data Sufficiency questions, answers, and videos.
Whichever method you choose to prep with, it is essential to read through study materials thoroughly and follow the preparation models that they have described in those materials. While most test-takers follow the above-prescribed study materials, some want to explore the test and its preparation independently. If you take that path, we recommend that your preparation method includes the steps below.
- Read a lot of formal write-ups like newspapers and technical documents with graphs, images with labels, etc.
- Spend time brushing up on high school math – algebra, geometry, etc.
- Download and use the free GMAP Prep software.
- Use a lot of practice tests throughout your GMAT preparation journey.
The Day Before the GMAT
The day before the exam is sometimes as important as the day of the exam. By taking these steps, you’ll set yourself up for a smoother and more confident experience on GMAT test day.
- Verify ID and Necessary Documents
Double-check the identification requirements for the GMAT. Ensure you have a valid, government-issued photo ID and other required documents. Prepare these items the night before to avoid last-minute stress. - Review Driving Directions and Logistics
Familiarize yourself with the driving directions to the test center. Check for potential traffic issues and consider using a navigation app for real-time updates. Take note of the parking situation at the test center. Plan to arrive at least 30 minutes before your scheduled exam time to allow for unforeseen delays. - Weather Check
Keep an eye on the weather forecast for the day of your exam. Dress accordingly and be prepared for any weather conditions that might affect your travel. - Relax and Avoid Vigorous Exercise
Engaging in strenuous physical activity can lead to fatigue. Instead, use light exercise or relaxation techniques to ease tension and promote a calm mind. - Prioritize Rest
Resist the temptation to stay up late cramming for the exam. The night before the GMAT differs from the night for last-minute intense studying. Ensure you get a good night’s sleep to be mentally sharp on test day. - Healthy Eating
Consume a nutritious and balanced meal the night before the exam. Avoid heavy or unfamiliar foods that might cause discomfort. Proper nutrition contributes to sustained focus during the test. - Select Section Order
Decide on the order in which you’ll tackle the GMAT sections. Consider your strengths and weaknesses, and choose an order that aligns with your preferences and concentration levels. Remember, you have the flexibility to decide the section sequence. - List Schools for Score Reporting
Make a list of the four schools to which you want your GMAT scores sent. This information is required during the exam registration process. Remember that reporting your scores to these schools is included in the GMAT fee. It may incur additional fees if you write scores to other schools later. - Organize Test-Day Essentials
Prepare a bag with all the essentials you’ll need on test day, including your ID, confirmation email, snacks, and any permitted comfort items. Having everything organized in advance reduces stress on the morning of the exam. - Relaxation Techniques
Incorporate relaxation techniques into your evening routine, such as deep breathing or meditation, to help calm nerves and promote a restful night’s sleep. - Visualize Success
Take a few moments to visualize yourself entering the test center confidently, managing the exam sections effectively, and completing the GMAT. Positive visualization can boost confidence and reduce anxiety. - Technology Check
Ensure your computer and internet connection are working well. Restart your computer to clear any potential issues. If possible, run a system check on the GMAT exam platform to ensure a smooth experience. - Emergency Contact
Share your test day plan with a friend or family member who can serve as an emergency contact. Provide them with details such as the test center location and your estimated return time. - Plan for Breaks
Familiarize yourself with the location of restrooms at the test center. Plan when you will take the optional breaks during the exam to maximize your efficiency and minimize disruptions. - Stay Positive
Remind yourself of your preparation and the effort you’ve put into getting to this point. Maintain a positive mindset and trust in your abilities.
GMAT Test Day Instructions
Remember, maintaining a composed and focused mindset on test day is crucial for achieving your best possible GMAT score. Follow these instructions diligently to ensure a smooth and successful testing experience.
- Device-Free Zone
Leave your cell phone and other electronic devices at home. Test centers strictly prohibit using personal items during the exam, and any violation may result in dismissal. - Arrive Early
Aim to arrive at the test center at least 30 minutes before your scheduled exam time. This allows for a smooth check-in process and helps you mentally prepare for the GMAT. - Identification and Documentation
Present your valid, government-issued photo ID and any required appointment documentation during check-in. Provide the necessary identification to be allowed entry to the test. - Maintain Calmness
Stay calm and composed throughout the exam. Expect to encounter challenging questions, but it’s crucial not to panic. Some questions may be time-consuming or complicated, but managing your time wisely is essential. Make informed decisions on whether to spend more time on a particular question or to move on swiftly to the next one. - Strategic Time Management
Recognize that time management is critical. Some questions may be designed to be more challenging, but spending too much time on a single question can negatively impact your overall performance. Strategically decide when to invest more time and when to make a quick, informed choice to maintain a good pace. - Pacing Tips
Remember that the GMAT is a timed test, and you won’t have unlimited time for each question. Prioritize completing the entire test within the allocated time. Use breaks strategically to refresh your mind without losing valuable time. - Unofficial GMAT Score
Immediately after completing the exam, you’ll receive an unofficial GMAT score. You have the option to either accept the score or cancel the exam. Take a moment to consider your performance and decide whether you are satisfied with the results. Note that if you choose to cancel, the score will not be reported to schools, and you may retake the GMAT later. - Post-Exam Procedures
Follow any additional instructions the test center staff provides. If you accept the score, you will receive an official score report later. If you canceled, you may make arrangements to retake the GMAT. - Maintain Test Integrity
Adhere to the test center’s rules and regulations to ensure a fair and secure testing environment. Any breach of these rules may result in consequences, so following all instructions is essential. - Collect Personal Belongings
Retrieve any personal belongings stored during the exam. Be mindful of test center policies regarding the handling of personal items. - Exit Calmly
Exit the test center calmly and quietly. Avoid discussing specific exam content with others to maintain test integrity. - Reflect and Plan
Take a moment to reflect on your performance after leaving the test center. Consider areas of strength and potential improvement. If necessary, plan your next steps for retaking the exam or moving forward with the application process.
Schools that don’t need GMAT
Many schools offer online masters programs. Most schools want a GRE or a GMAT exam results to be reported. However, more schools take a holistic approach to entrance criteria. Some of these schools either don’t need a GMAT or waive the GMAT requirements for students that meet the requirements, such as
- A good GPA in the undergrad degree
- A student has an accredited graduate degree in any other discipline
- A student that has a professional certification such as a CPA or CFA, etc.
- A certain number of years of experience as a professional
Here is a list of such schools that don’t need a GMAT for admission into their online master’s programs.
GMAT FAQs
Frequently Asked Questions
Is GMAT hard?
No, the difficulty of the GMAT largely depends on your preparation. With thorough and effective preparation, the GMAT can be manageable. The key is to create a strategic study plan and dedicate sufficient time to mastering the content and test-taking strategies.
Are Calculators Allowed in GMAT?
How Long Should You Prepare for the GMAT?
How Many Questions Are on the GMAT?
How to Prepare for GMAT?
What Does the GMAT Test Include?
What Is a Good GMAT Score?
How Many Times Can You Take the GMAT?
How Long Do GMAT Scores Last?
How Long Does It Take to Get GMAT Scores?
What are the differences between a GMAT and GRE score?
Is the GMAT Test Available in an Online Format?
Can You Cancel a GMAT Score After Leaving the Test Center?
What is the Cost of Rescheduling or Retaking the GMAT?
Are There GMAT Test Centers Worldwide?
Are There Any Breaks During the GMAT Exam?
How to Interpret the GMAT Score Report?
Can I Use Scratch Paper During the GMAT?
How Soon Can You Retake the GMAT if Unsatisfied with the Score?
What is the Test-Day Experience Like in the GMAT Online Exam?
Additional GMAT Resources
- The Grad Café/ – GMAT/GRE Forums: The Grad Café is a dynamic online forum where GMAT and GRE test-takers can engage in discussions, exchange ideas, and seek help from a community of peers. It provides a platform for sharing experiences, study tips, and mutual support.
- MBA.com: MBA.com is the official website of the Graduate Management Admission Council (GMAC), which administers the GMAT. It is a comprehensive resource providing all the information you need for the GMAT. This includes details about the exam structure, registration, official study materials, and an 8-week study plan to help you organize your preparation effectively.
- Magoosh GMAT Blog: Magoosh, known for its GMAT preparation services, offers an insightful GMAT Blog. This blog is a valuable resource covering a wide range of GMAT topics. It provides in-depth articles on studying strategies, score-improvement techniques, and test-taking strategies. Whether you are a beginner or an advanced test-taker, the Magoosh GMAT Blog has content suitable for all levels of preparation.
- Beat the GMAT: Beat the GMAT is a comprehensive platform that offers a variety of GMAT study materials. It serves as a resource hub, including study plans, practice questions, and forums where you can connect with other test-takers. Beat the GMAT also provides expert advice, webinars, and success stories to inspire and guide you through your GMAT journey.
- Discover Business: Discover Business is a valuable resource for GMAT test-takers seeking detailed strategies for each section of the exam. The platform provides comprehensive insights into study approaches, tips for exam sectiond common mistakes to avoid. It is a go-to destination for those looking to enhance their understanding of the GMAT content and improve their overall performance.
- Quizlet: Quizlet is a versatile and free tool that allows users to create flashcards for various exams, including the GMAT. Test-takers can leverage Quizlet to reinforce their knowledge of key concepts, definitions, and formulas. The platform also offers collaborative features, enabling users to access and share flashcard sets created by others, fostering a collaborative learning environment.
Find Your Master’s Program
Start Your Next Step Today
Let’s help you find the right online master’s degree. You can browse through thousands of schools and their online programs. Start exploring the top 20 best online master’s programs now.